China launches powerful space X-ray observatory satellite for violent cosmic phenomena observation
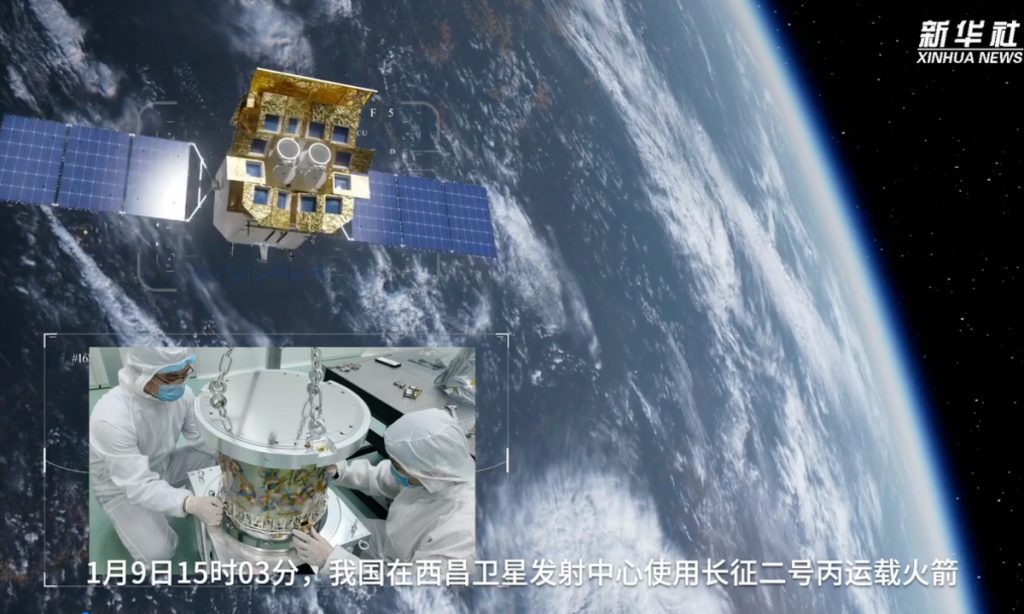
China successfully sent on Tuesday a new-generation X-ray observatory satellite, the Einstein Probe (EP), into orbit to monitor flashes in the night sky and observe mysterious transient phenomena in the universe. The satellite will help reveal more about this violent and little-known side of the cosmos and help advance people’s understanding of tumultuous cosmic events.
The satellite lifted off atop a Long March-2C rocket from Xichang Satellite Launch Centre in Southwest China’s Sichuan Province at 3:03 pm, China’s National Space Science Center (NSSC) of Chinese Academy of Science announced on its website.
According to the NSSC, the EP is a scientific satellite among the Strategic Priority Program on Space Science (II), a series scientific satellites program implemented by China since 2011 following the successful launches of scientific satellites such as Wukong and Mozi satellites.
The Einstein Probe Space Science Satellite serves as a cosmic explosion catcher, capable of precisely capturing more distant and fainter transient sources and eruptive celestial bodies. It explores X-ray signals from sources of gravitational waves and holds important scientific significance in studying the formation, evolution and mergers of dense celestial objects such as stars, black holes and neutron stars.
The EP satellite employs the time-domain astronomy in the soft X-ray band to conduct high-sensitivity real-time dynamic sky surveys, in a bid to systematically discover high-energy transient and variable celestial objects, monitor the activity of already known celestial bodies and explore their natural and physical processes.
With the new X-ray detection technology inspired by the functioning of a lobster eye, the EP weighs1.45 tons and it’s as large as a full-size SUV. It is shaped like a lotus in full bloom and features 12 petals and two stamens.
The “petals” are actually 12 modules consisting of wide-field X-ray telescopes, while the two “stamens” consist of two modules of follow-up X-ray telescopes.
With these instruments, the EP can conduct wild-field surveys while accurately capturing distant and faint high-energy transient sources in the universe, as well as capturing transient unknown phenomena. It issues alerts to guide ground-based and other astronomical facilities for subsequent observations.
The satellite is designed to last 5 years.