‘One of a kind’ mainland-Macao satellite a result of intl collaboration: chief scientist

The "Macao Science 1" satellite that the Chinese mainland and Macao co-developed was "one of a kind" featuring great uniqueness and innovation. It is a result of international collaboration by leading scientists from around the world and has in turn attracted many Western institutes to join the work, Zhang Keke, chief scientist of the "Macao Science 1" satellite, told the Global Times in an exclusive interview.
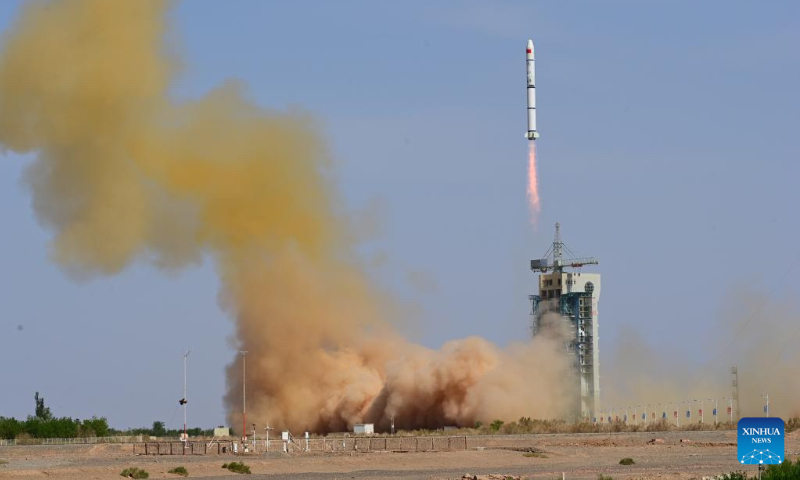
Two "Macao Science 1" satellites were successfully launched into orbit on May 21, 2023, marking the first space science satellite program jointly developed by the Chinese mainland and the Macao Special Administrative Region.
Macao Science 1 takes a twin-satellite approach. Satellite A carries payloads including high-precision magnetometers to detect Earth's magnetic field. Satellite B is equipped with payloads like high-energy particle detectors and solar X-ray instruments to obtain space environment data.
Satellite A is the world's first low-latitude geomagnetic field and space environment scientific detection satellite, featuring the highest geomagnetic field detection accuracy in China. It will significantly improve the level of the country's space magnetic measurement technology, according to the China National Space Administration.
During an exclusive interview with the Global Times, chief scientist Zhang Keke said that they are now carrying out in-orbit testing, which is expected to be completed by the end of this year, after which they will collaborate with Western and domestic scientists to conduct scientific research based on the data obtained.
Zhang told the Global Times that the research and development of the satellite is the most challenging among all satellites of this type.
For one thing, the satellite must be non-magnetic to avoid inducing its own magnetic field, and its measuring instrument needs to be far away from all electronic instruments, generators, and other equipment.
Therefore, it was designed into a unique shape with a box sticking to the end of a long pole, extending to eight meters. This means that it has to be folded up during the rocket launch and unfold after arriving in orbit.
"When everyone was cheering for the success of the launch back then, I was actually very nervous as we waited for the pole to fully unfold. It took about two hours before we knew the unfolding maneuver had been performed perfectly," Zhang recalled.
When asked if his team has encountered any restrictions in its collaboration with Western scientists given the tense relationship between China and the US, Zhang said it wasn't an issue since "for us scientists, there should not be limitations in cooperation due to the so-called decoupling, as science knows no borders."
Many technical problems were difficult to solve, and they received help from researchers from European countries during the R&D process, Zhang said. He is now leading a team of about 30 scientists, some of whom are from the Chinese mainland and Macao, while others are from the US, UK and France among other countries.
What's more, they have signed agreements to jointly conduct research on the satellite with 18 top research institutes from around the world, including those from France, the US, the UK, and Germany.
"Westerners came to us, not the other way around," Zhang said proudly, as he introduced the unique advantages of the satellite. "The scientific project you are working on must be of interest to others, and that means it must be a first in the world. Our satellite is the first high-precision Earth magnetic field measurement satellite launched at a low inclination angle, which is of great significance to scientific advancement."
The expert further explained that the existing high-precision Earth magnetic field measurement satellites are polar satellites, mainly measuring the changes in physical parameters from the South Pole to the North Pole. And the Macao Science 1 has filled in a gap for east-west directions.
Elaborating on the importance of studying Earth's magnetic field, Zhang said that it not only provides a protective shield that blocks high-energy charged particles from the Sun from entering the atmosphere, but applies to almost every area of human beings' daily lives.
"Living on Earth, we need to know how changes occur and what changes will happen in the future. And that's really a question of the movement of the Earth's magnetic field," Zhang said.
Scientists generally believe that the magnetic field occurs in the Earth's core more than 3,000 kilometers below the surface. It is extremely hot at over 5,000 C, mainly consisting of molten iron. This produces a lot of kinetic energy, which is converted into magnetic energy, thus producing a magnetic field.
However, as humans can only drill down into the Earth's surface to a depth of 12 kilometers, we cannot see anything. The only way is to observe the changes of the Earth's magnetic field in time and space, requiring the use of satellites.
This is essential for satellite navigation for airplanes, ships, and spacecraft, which is very important for a country's economy, industry, and national security.